With the continuous improvement of people’s requirements for drug safety, the national drug regulatory department is also increasing the supervision of pharmaceutical companies. In order to adapt to the rapid development of the pharmaceutical industry, it is particularly critical for companies to do a good job in production site management and quality monitoring. Combining the requirements of relevant laws and regulations on drug production and the 5S management concept, this paper expounds the on-site management and quality monitoring of drug production, and provides suggestions and references for the rational operation of the drug production quality management system of pharmaceutical companies.
Drug production site management and quality monitoring are an important management content in drug production activities. The purpose of production site management and quality monitoring is to improve efficiency and meet the requirements of GMP, that is, to ensure quality and increase output.
The on-site management and quality monitoring described in this article mainly refers to the on-site management involved in quality monitoring. 5S management originated from Japan, and its basic contents are sorting, rectifying, cleaning, cleaning, and literacy.
1 On-Site Management Under GMP Requirements
Article 3 of Chapter 1 (General Provisions) of the 2010 version of GMP in the relevant regulations on drug production stipulates: This specification, as part of the quality management system, is the basic requirement for drug production management and quality control, and aims to minimize the risks of contamination, cross-contamination, confusion, errors, etc. in the production process of drugs, ensuring the continuous and stable production of drugs that meet the intended use and registration requirements [2].
Strengthening on-site management is a concrete manifestation of the implementation of GMP. On-site management objectives: the site is clean and orderly; the marking is complete and clear; the records are filled in truthfully, completely, accurately and timely; the operation conforms to the SOP. On-site management mainly includes personnel management, hygiene management, material control and identification management.
1.1 Personnel Management
Personnel Management Should Meet The Following Requirements:
(1) Post personnel should be familiar with SOP and master its related skills.
(2) Batch production records, equipment operation records and other related auxiliary records should be filled in in a timely, true, complete and accurate manner.
1.2 Hygiene Management
Hygiene Management Should Meet The Following Requirements:
(1) Sanitary ware management should be classified and neat.
(2) Work clothes should be cleaned on time and separately.
(3) Standard dressing procedures shall be implemented for dressing requirements.
(4) Production cleaning and disinfection should be carried out in accordance with regulations and corresponding records should be kept, and the selection and regular rotation of disinfectants should be carried out.
1.3 Material Control
Material Control Should Meet The Following Requirements:
(1) The status identification is clear and the information is complete.
(2) The card, account, and quantity are consistent with the physical object.
(3) The release control is clear, and the quality supervisor participates in the control.
(4) Special material management (unqualified materials, returned products, samples, etc.) has a specified area, which is isolated, marked and recorded accordingly.
(5) The storage conditions should meet the storage requirements of materials and products, and have complete records.

1.4 Identity Management
Identity Management Should Meet The Following Requirements:
(1) Documents and records should have valid version control identification.
(2) The equipment should be marked with status, such as intact, running, pending repair or deactivated.
(3) All containers should be marked with cleanliness and expiration date.
(4) The production area should be marked with cleanliness and usage.
(5) Each production process should be marked with production status.
(6) The public system and the system in the production area should have a floor plan, and the corresponding pipeline should have the medium name and flow direction identification.
(7) Various types of measuring instruments should have measurement qualification information and expiration date marks.
(8) Facilities such as buildings and rooms should be managed by serial numbers.
2 Common Defect Clauses At The Production Site
The occurrence of quality problems is often caused by loopholes in management, which is reflected in the ineffective implementation of GMP in an all-round way, the failure to implement the management system, the lax checks at all levels, and the insufficient implementation standards [3]. Various types of defect clauses will appear on the production site. The types of clauses mentioned in this article, including the clauses concerning data reliability, are summarized into three types: production management, material and product management, and quality system. Some common defect clauses will be briefly described in each type.
2.1 Production Management
(1) In the production process, records are filled in advance, records are not filled in synchronously, records are not filled in truthfully, records are filled in irregularly, and relevant records are lacking. For example, if an enterprise inspects defects: there is no record of equipment use at the production site, and records are not provided during data inspection [4]. The challenging test conditions of the vertical steam sterilizer for medium sterilization are 121°C, 30 minutes, and the actual medium sterilization parameters are 121°C, 20 minutes, and the sterilization period is not recorded [4]. The batch production record of a certain granular product (batch number 20180605) has irregular weighing figures, and some records in the production workshop are arbitrarily modified without signature [4].
(2) There are no relevant signs on the production site or the signs are not clear, and the relevant information does not correspond to the actual status in a timely manner. For example, the inspection defect of an enterprise: the clean clothes in the external workshop and the sanitary ware hanging between the sanitary ware have no clean status mark [4]. The status plate of the alcohol precipitation tank equipment of Building H does not indicate the product name [4].
(3) The storage of sterilized supplementary bottles/bags and production molds is not locked and managed as required. For example, the inspection defect of an enterprise: the mold storage is not locked and managed, and there is no use of the ledger [4].
(4) Disinfectants are not managed in strict accordance with regulations, there is no relevant record in the preparation process, no expiration date or expired use is specified, and the type of disinfectant is single. For example, the inspection defect of an enterprise: the disinfection record of W010 sanitary ware room shows that it was disinfected in August 2017, and there is no other disinfection record.
(5) The placement of the electronic scale in the weighing process is not stable, the calibration weights are not placed on site, and the storage of the weights is not standardized. For example, the inspection defect of an enterprise: the standard weight (No. 444) used in the soft capsule production workshop is valid until June 18, 2018 and has expired; the warehouse uses a 1 kg/5 kg standard weight to calibrate the electronic scale. The standard weight is not marked, the validity period is not clear, and the storage is not standardized [4]. The countertop of the electronic scale (SCRG-D011) placed in the weighing room of the external workshop is easy to shake and is not stable, and no calibration weights are placed on site [4].
(6) Relevant environmental monitoring was not carried out in the key areas of the clean area, and the daily environmental monitoring indicators were abnormal, and no deviation investigation was carried out.
(7) When abnormal data occurs in the production process detection indicators, no deviation investigation is carried out, and the operation is directly carried out to the next process.
(8) Relevant guidance documents and records are not placed on the production site.

(9) Dirty, messy and poor environmental sanitation at the production site was not cleaned up in time.
2.2 Material And Product Management
(1) The storage area is not monitored for temperature and humidity, and there is no insect-proof and rodent-proof facility. For example, a defect in the inspection of a certain enterprise: there is no temperature and humidity monitoring in the C area of the medicinal material warehouse [4].
(2) There is no reviewer reviewing the material warehousing or distribution process, and the material receiving and distribution ledger has not been registered. For example, the defect inspected by an enterprise: In the raw grass black YPA8A000 cargo space card, there is only one sender and receiver, and no double issuance is performed [4]. The enterprise failed to provide the receipt and distribution ledger of auxiliary materials [4].
(3) The materials after storage have no status identification, and the sampling label is not affixed in time after sampling. For example, the inspection defect of an enterprise: 280 pieces of goods that were put into the warehouse in May 2018 are pending inspection, but they do not reflect that they should be sampled, and there is no sampling label on the packaging [4].
(4) The materials are not placed according to the regional classification, there is no corresponding location card, the information of the location card does not match the physical quantity, and the filling of the location card is not standardized. For example, the inspection defect of an enterprise: the material management is chaotic, the inventory material does not have a cargo card, and the incoming and outgoing quantity is not recorded [4].
(5) The storage of text packaging materials is not managed by a special person with double locks as required. For example, the inspection defect of a certain enterprise: there is no corresponding record for the receipt of materials in the packaging material warehouse and the label warehouse, only the specifications, quantities and other information are simply recorded on the notebook hanging at the entrance, and there is no record of the whereabouts of the materials; the management of the label transfer warehouse in the workshop is not perfect, the label cabinet is not locked and managed, there is no special person to manage, and there is no record of label receipt [4].
(6) The production surplus materials are returned, the warehouse has not done the labeling and identification, and the packaging does not meet the requirements.
(7) Special materials (unqualified materials, returned materials) are not placed in isolation.
(8) The returned products are not placed in the return warehouse as required.
(9) Materials that have reached the re-inspection period have not been re-inspected as required, and are directly put into production.
2.3 Quality System
(1) The company has no training plan, and the personnel training files are not perfect. For example, the inspection defect of a certain enterprise: random inspection of individual personnel training files, only a sign-in form, no training content [4].
(2) The transfer personnel did not carry out the corresponding transfer training and assessment.
(3) Insufficient staffing of quality assurance and quality control personnel in the enterprise.
(4) The batch production record design is not standardized. For example, the inspection defect of an enterprise: the batch production instruction only has the signature column of the writer and the reviewer, and there is no signature column of the issuer [4].
(5) Failure to conduct supplier approval in strict accordance with the requirements. For example, if an enterprise inspects defects: the filing information of the supplier of a certain extract powder product is not displayed in the “Annual Supplier Comprehensive Review Form”, which has the conclusion that it agrees to continue as a supplier, and there is no authorized signature for approval [4].
(6) The verification content in the verification scheme is unreasonable. For example, the inspection defect of an enterprise: the verification scheme of ozone disinfection effect in the non-sterile sampling room of the warehouse is unreasonable, and the indicators such as the effective concentration of ozone have not been confirmed [4].
(7) When there is a deviation, the deviation processing procedure is not carried out, and the deviation is closed in a hurry if the deviation investigation is not thorough when the deviation process is executed.
(8) The annual quality review analysis of the product is unreasonable. For example, a company inspects defects: in 2017, the company randomly selected 4 batches for the quality review of deer antler, and randomly selected 3 batches for the quality review of red ginseng, and did not conduct quality analysis on all the batches produced in the year [4].
3 On-Site Quality Monitoring Integrating The 5S Concept
Improving the quality of medicines helps to improve the viability of enterprises in the market competition. In the course of operation, drug production enterprises should establish and improve the corresponding drug production inspection system, which not only provides reference standards for each link of production and processing, but also provides guarantee for drug production technology and drug production management. Therefore, in order to further improve the quality management supervision level of drug production enterprises, it is necessary to actively take effective measures [5]. Now analyze the on-site quality monitoring methods that integrate the 5S management concept.
3.1 Scope Of Quality Monitoring At The Drug Production Site
The scope of quality monitoring at the drug production site is divided into six elements: human, machine, material, method, environment, and others. (as the picture shows)
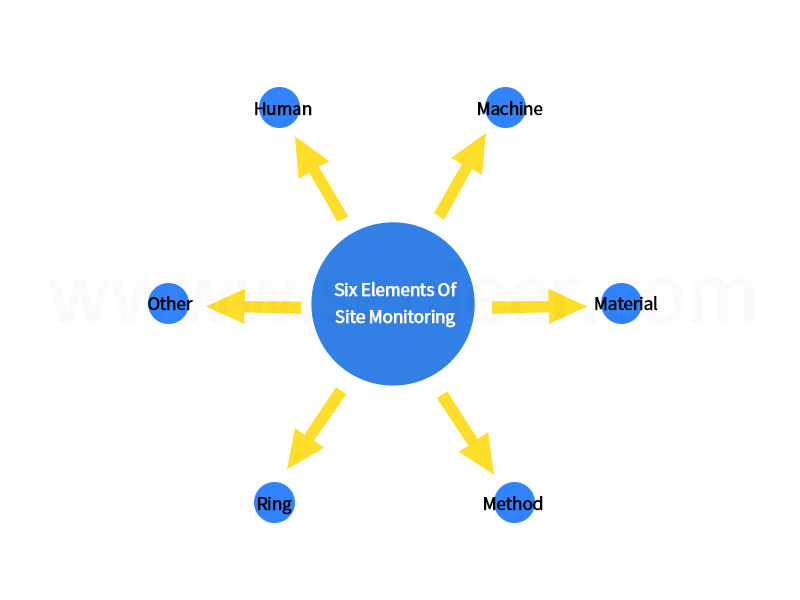
Six Elements Of On-Site Monitoring
3.2 On-Site Monitoring Methods
On-site monitoring methods are divided into the following types:
(1) Ask the relevant personnel to understand the corresponding responsibilities and the implementation of GMP.
(2) On-site inspection of the production site (such as materials, labels, etc.), material storage, and sanitation.
(3) Check documents and records, and check relevant procedures and records.
3.3 Contents And Measures Of Quality Monitoring
3.3.1 People
Person: refers to the person who directly or indirectly affects the quality of the product, including production operators, workshop managers, monitoring personnel, and inspection personnel. Monitoring includes:
(1) Skills: Personnel should receive training before taking up their posts, and should have the ability to operate independently.
(2) Qualification: Personnel should be able to adapt to the environment and understand methods.
(3) Training: Personnel should receive induction training and continuous training, and be familiar with SOP.
(4) The responsibilities of each person should not be too much.
(5) Personal hygiene and dress should meet the requirements.
(6) The production personnel should fill in the batch records and other records correctly in a timely manner, the content of the records should be consistent with the content of the site, and the production operation process and parameter control should comply with the technical regulations.
(7) Weighing, batching, and feeding should be reviewed by an independent reviewer. The material label should be filled in and pasted in time, and the material information can be correctly indicated and the quantity is correct.
(8) Monitor the production site, environment, materials, production equipment, process parameters, personnel operations, and key control points of product quality.
(9) The records should be filled in timely, accurately and truthfully.
(10) Foreign personnel entering the control area should be trained and approved.
(11) Personnel should not appear to be able to deal with but not deal with the situation.
Monitoring measures: Access personnel files, training materials, records, and on-site inspections.
3.3.2 Machine
Machine: refers to the equipment, instruments and other auxiliary appliances used in production inspection. Monitoring includes:
(1) The use of the equipment should be verified and confirmed within the validity period of the verification.
(2) The preventive maintenance plan and operation of the equipment should be formulated and recorded.
(3) The equipment operator should be able to use the equipment correctly.
(4) The instruments and equipment that need to be calibrated should be calibrated regularly, the measurement management should be managed by a special person, and the calibration institution should be qualified.
Monitoring measures: Check the equipment files, check that the relevant provisions of the preventive maintenance plan in the documents should be consistent with the actual records, check the equipment use records, check the equipment verification materials, check the calibration records and calibration certificates of the instruments and on-site inspections.

3.3.3 Materials
Materials: refers to raw and auxiliary materials, packaging materials and process water. Monitoring includes:
(1) The incoming manufacturer should be an approved and qualified supplier.
(2) The materials used should be approved for release.
(3) The material should be weighed in accordance with the prescribed amount of the process.
(4) The process water should be tested regularly, and the water system should be cleaned and disinfected according to the prescribed cycle.
(5) The material storage conditions should be met during the storage period.
(6) The material status identification should be clear, the information should be complete, and the card and account should be consistent with the physical quantity.
Monitoring measures: Check the list of qualified suppliers and on-site inspection.
3.3.4 Method
Law: refers to the quality management document system. Monitoring includes:
(1) The inspection document system shall comply with GMP regulations and relevant laws and regulations.
(2) The description of the inspection file system should be clear and easy to understand.
(3) The document system should run through the whole process of drug production and sales.
Monitoring Measures: Check The Corresponding Documents.
3.3.5 Ring
Ring: Refers to the general area and the clean area. Monitoring includes:
(1) The environment should not exceed the standard index during the cleaning period.
(2) The luminosity, temperature, humidity, differential pressure, microorganisms, etc. shall meet the technological requirements.
(3) The production environment should be safe and orderly.
(4) Hygiene Management: Sanitary ware should be classified and managed neatly, work clothes should be cleaned on time and separately, clothes should be changed according to standard changing procedures, production cleaning and disinfection should be carried out according to regulations and corresponding records should be kept, and disinfectants should be rotated regularly.
Monitoring measures: Check environmental monitoring records and on-site inspections.
3.3.6 Others
Other: Refers to identification management, deviation, change, verification. Monitoring includes:
(1) Identification Management: Documents and records should be effectively version controlled, equipment status identification should be clear, various containers and production area clean status identification should be clear, public system pipeline identification should indicate the content and flow direction.
(2) Deviations And Changes: All deviations and changes should be effectively resolved, and the closure should be reviewed and approved by the Quality Management Department.
(3) Verification: All verifications related to product quality can be effectively implemented and within the validity period of verification.
Monitoring measures: Check deviation and change records and ledgers, check verification documents and on-site inspections.
3.4 Timing And Focus Of On-Site Monitoring

3.4.1 Before Production
Check before production to confirm whether the production site has been cleaned according to standard cleaning procedures, and no material unrelated to the product to be produced is allowed in any part; the production environment should meet the production process requirements; the raw and auxiliary materials, semi-finished products, and packaging materials used in production etc., the type and quantity should meet the production process requirements; the key process parameters should be set in accordance with the production process documents; the corresponding production documents should be placed on site for easy access.
3.4.2 During Production
During the production process, the production site, environment, materials, production equipment and process parameter settings should be reconfirmed regularly to ensure that the above production conditions always meet the production process requirements; the quality characteristics of the produced products should be inspected and monitored regularly, and the inspection results should be in line with process control standards and product quality standards, some unstable quality factors should be monitored for fluctuations to ensure that the process is always in a stable state.
3.4.3 Post Production
After the production is over, the production site and equipment should be cleaned in time according to standard cleaning procedures, and the remaining materials and waste materials should be removed from the production site as required.
4 Conclusion
Only by establishing a sound drug production quality management system and strictly implementing it can drug manufacturers have a good grasp of the drugs they produce, so that each batch of drugs can be put on the market and serve the general public. The new version of GMP is embodied in the quality concept of full participation, that is, all personnel in the enterprise should participate in the production quality management work. The implementation of the production quality management standard of the whole process and all indicators within the company, supplemented by scientific management methods, helps to ensure the scientific, standardized and practical production quality management work. Pharmaceutical manufacturers should always make unremitting efforts to improve the production quality management system, continuously improve product quality, and improve user satisfaction.










