What is trituration?
Trituration is the name of various different materials processing processes. In some ways, it is a type of milling (reducing the particle size of a substance). In another meaning, it is the process of producing an uniform powdered material by completely combining and crushing constituent ingredients.
The trituration method entails pressing or crushing solid powder in a mortar and pestle. The trituration process is utilized for pulverization as well as mixing.
The trituration procedure entails pounding or crushing hard powder in a mortar and pestle. The trituration process is utilized for pulverization as well as mixing.
Trituration in a mortar thoroughly mixes crystalline salts. Long-term use smooths the inner surface of mortar rows. Powders do not mix well when this occurs. In such cases, the surface of a mortar can be roughened by triturating it with a little amount of powdered medicinal sand.
In those problems we can say:
-
Electrification
Electrification is a phenomena that occurs when certain compounds reject each other upon combining. This could be owing to simple resistance to mixing or to electrical charges.
This issue can be solved by simply moistening the granules with a few drops of alcohol or mineral oil.
-
Storage
When particles are strongly squeezed during trituration, a packaging difficulty occurs. This issue can be prevented by triturating lightly and scraping the sides of the mortar with a spatula on a regular basis.
-
Physical incompatibility
Physical immiscibility can sometimes cause small complications. Combining resinous compounds with granular salts, as well as combining a heavy powder (starch) with a light powder (zinc stearate), may result in this incompatibility.
This issue can be mitigated by triturating each material individually to a fine condition before mixing via sifting or tumbling.
-
Liquification or damping
Dampening, or liquefaction, is the most troublesome problem in powder mixing and can happen for three different reasons:
a) Air moisture absorption (deliquescent/hygroscopic)
A hygroscopic substance is one that collects moisture from the air). Deliquescent materials are hygroscopic materials that collect moisture from the air to the point where they partially or completely liquefy.
Hygroscopic materials shouldn’t be crushed finer than necessary and they must be stored in well sealed containers.
b) Releasing moisture into the air and liquefying in the process (efflorescent)
Atropine sulfate, quinine HCl, and scopolamine hydrobromide are a few examples.
There are three(3) main options for dealing with this issue:
- Dispense the different components separately.
- Each chemical is diluted with an equal amount of inert diluents (lactose, starch) before being combined with light trituration.
- Allow the ingredients to liquefy before adding enough adsorbents to adsorb the eutectic liquid mixture while remaining as a free-flowing powder.
Why choosing senieer?
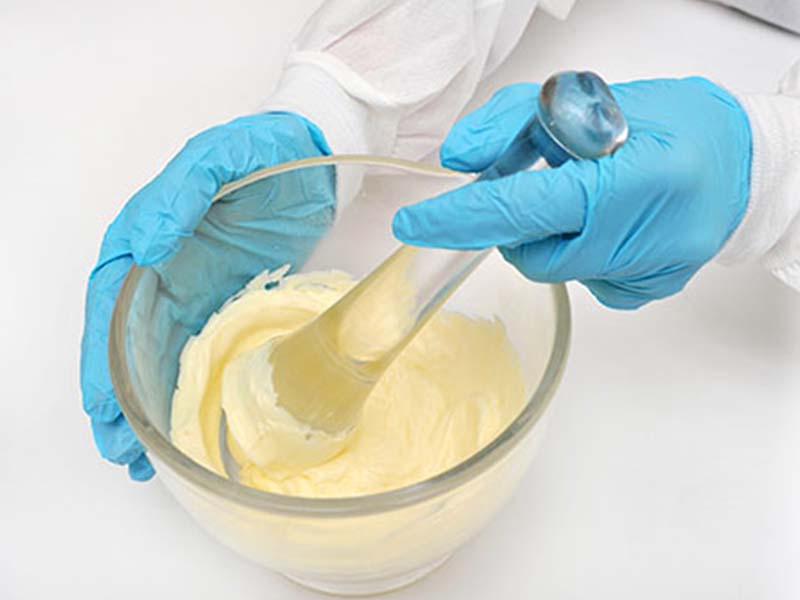

Senieer, a global leader in pharmaceutical equipment manufacturing and distribution, offers a ONE-STOP SOLUTION. Senieer is the leading global partner for pharmaceutical, food, chemical, and cosmetics firms. For almost 34 years, Senieer has primarily focused on solid dosage forms in China. Dependable integrated process solutions. We produce equipment in compliance with international standards such as GMP, cGMP, and the US FDA.
Members of the Senieer technical team enhance one-stop solution services for large-scale projects, from consulting through design. We fully fulfill your approach and requirements for resolving all of your concerns.










