As macromolecular drugs, biological products are relatively complex in structure and function, and their efficacy is mostly directly related to their biological activity. Due to the high-quality and active characteristics of biological products, most biological products cannot be terminally sterilized, so the control of their production process is more stringent, and each step in the process needs to strictly control microbial contamination and endotoxin residues. And it is necessary to strictly implement the cleaning procedures between batches and within batches to achieve complete removal of residual protein. It is necessary to ensure that there is no residue of the host protein, but also to ensure that there is no residue of the target protein, so as to maximize the safety of the patient’s medication.
The essence of the cleaning verification of biological products is a process verification, which is to treat the cleaning method as an important process step. For the risk management of the whole life cycle of the drug, to ensure the continuous effectiveness of the cleaning method, and with the production process. Changing the cleaning process or cleaning method will also bring some changes. Therefore, the effectiveness of the cleaning process should be regularly evaluated.
Risk assessment of cleaning process. As a tool for effective control of drug quality, risk assessment methods have been widely used in various pharmaceutical fields. The activity of cleaning validation itself has a strong need for risk assessment in terms of importance and complexity. It is also required by regulatory authorities.
Risk Identification
Identify hazards from the environment, equipment, methods, chemical and microbiological entities, and people. These hazards may have an impact on the final residue after cleaning and are therefore considered risks.
Risk Analysis
These risks are further analyzed to better understand the process and then prioritized based on their impact on cleaning. During this phase, process knowledge is augmented through design reviews, data reviews, and studies to understand the interactions between process parameters, equipment, environment, and people.
Risk Assessment
Assess risk and identify additional controls to reduce risk(Risk reduction)or accept the risk(risk acceptance).
Risk Control
During the risk control process, a final decision on acceptable risk is made and a control strategy is finalized to ensure that mitigation design, procedural and technical controls are implemented and remain in place. This control strategy is formally communicated to stakeholders.
Risk Review
Risk reviews should be conducted periodically or when significant or new hazards arise, such as the introduction of new products, after a major event or activity.
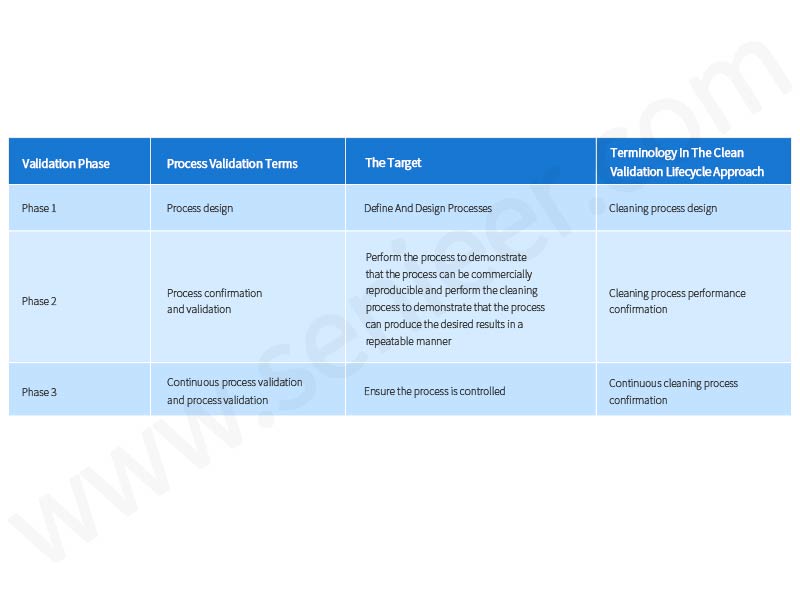
Cleaning Validation Phases and Objectives
One of the core elements of cleaning verification is the development of cleaning processes. The cleaning process developed based on product characteristics can ensure that products are free from various contamination. In the process of cleaning process development, the type and concentration of cleaning agents, cleaning methods, continuous The important process parameters such as time and temperature are comprehensively developed, and there is enough operating space to ensure the cleaning effect. Even when the cleaning equipment, personnel, and cleaning agent fluctuate to a certain extent, the cleaning effect can be guaranteed.
Since the development of the cleaning process itself involves the material of the equipment to be cleaned, the type of residue, the type of residue, and the retention time of the dirty equipment(DHT),ATCTDue to the interaction of multiple input parameters, various elements will interact, so it is a reasonable way to use the method of experimental design to develop the cleaning process.
Through the method of experimental design, the operation space of the cleaning process is explored, so that it can be carried out smoothly during the formal verification of the cleaning process. For example, in view of the characteristics of biological product production, in the upstream production process, the types of materials are very complex and it is difficult to completely define the residual amount, and because of the different process sections of buffer system and medium preparation The resulting differences in residues, permissible limits and residual substances also lead to different cleaning methods, and the resulting development of cleaning processes will be diverse and need to be considered in parallel.
After the cleaning process development is completed, it is necessary to enter the formal commercial production workshop to carry out specific cleaning process transfer. Due to the complexity of the biological product production process, the cleaning process developed in the laboratory needs to be accurately transferred to the production system. The technology transfer of the process will become particularly important. Just like the process transfer, the enterprise should establish a technology transfer model for the cleaning process to ensure that the cleaning process developed in the laboratory stage can be effectively transferred. The current national regulations basically require that cleaning verification should be completed at least at the same time as the product is launched, and it should be continuously and effectively controlled in the subsequent production process to ensure its verification status.
Cleaning process development for biological products There are many special aspects in the production and cleaning process of biological products: cleaning methods are similar, such as purified water rinse, alkaline rinse, water for injection rinse,SIPWait. Cleaning methods for different bioprocesses may also be similar.
The regulations stipulate that materials for certain processes of biological products must be dedicated, such as chromatographic fillers, ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes, while general biological products companies rarely reuse consumables based on product value and risk considerations. customary, this situation requires consideration of cleaning validation of process equipment(collinear part)Possibly very few, especially in plants where single-use items are heavily used. The protein, which is the main pharmaceutical ingredient in the production process of biological products, is very easy to degrade, so the method of detecting active pharmaceutical ingredients in the cleaning verification of biological products may not be applicable, but the degraded substances may still be active.(sensitization). The pollutants of biological products in different process sections may be very different, so it is not possible to design uniform limit standards and test methods. Cleaning sampling methods The sampling methods for cleaning verification are usually two methods: wiping method and rinse water sampling. Visual inspection It is necessary, because if the visual inspection fails, the necessity of using physical and chemical inspection does not exist. It is generally recommended to use the wiping method as much as possible where the wiping method can be used.PDATechnical Reports49Several basic principles for exempting swab sampling are also proposed:
1, The equipment that cannot perform swab sampling and the equipment that can perform swab sampling have the same material;
2, equipment that is difficult to swab sampling is exposed to the same residues and conditions as the surface of equipment that can swab sampling;
3Clean hard-to-reach equipment surfaces using the same cleaning procedure as equipment capable of swab sampling(i.e. same detergent and same temperature);
4, The mechanical force for cleaning the piping system should be greater than that of the tank cleaned with the spray ball(For example, turbulent flow);
5, Compared with the tank, it is guaranteed to be completely filled with liquid when cleaning the piping system;
6, Shower sampling properly solves the problem of surface cross-contamination.
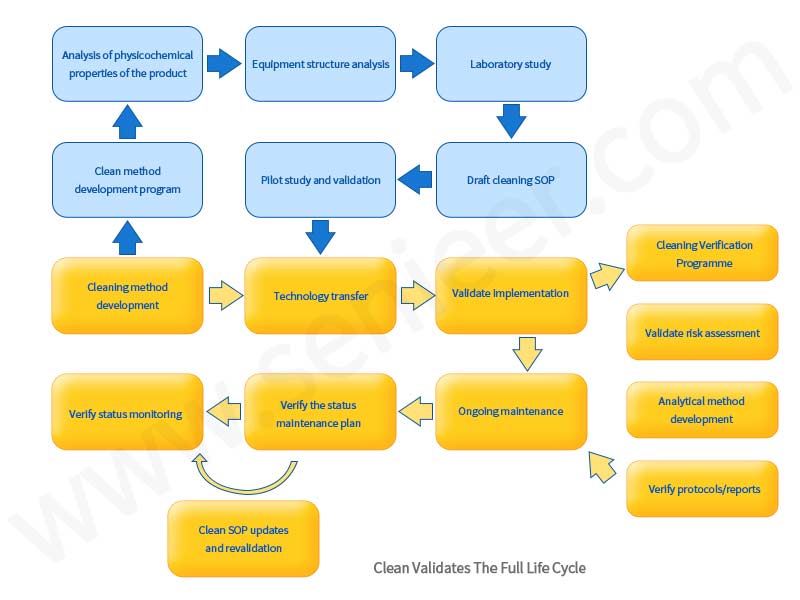
In the continuous validation stage of the cleaning process, continuous monitoring of the cleaning process is used to ensure that the cleaning process is running in a controlled state. The third stage mainly includes the following aspects:
1.Ongoing Cleaning Monitoring
Through process monitoring, some unplanned deviation events can be detected. Data from process monitoring should trend towards changes in cleaning method performance. Monitoring procedures should be risk-based and take care to establish hazards and confidence through cleaning validation. The monitoring program can be a subset of the tests used during cleaning process performance validation, should include a sampling plan, and should list all analytical methods to be used.
2.Periodic Review
As part of the validation life cycle, a comprehensive assessment of the cleaning process status is performed. The purpose of the review is to demonstrate that the cleaning process continues to be maintained in a state of validated control, and the results of periodic inspections may include recommendations for process improvement or revalidation if the cleaning process is found to be out of control.
3.Product Replacement Procedure(PCO)
PCOProcedures should be in place, risk-based approaches, combined with historical performance data, on which to run product replacement procedures.
4.Extra Control
Validated cleaning processes will be maintained in accordance with change control procedures. A preventative maintenance program is in place to keep the equipment running. Additionally, unexpected events representing failures of the cleaning process will be recorded as deviations. For example, each manual cleaning practice that does not meet acceptance criteria must be documented before re-cleaning is performed according to an approved procedure. The procedure should indicate an investigation requirement to track and trend all failures of a similar nature to further identify the root cause so that appropriate corrective and preventive actions can be taken, not just repeated cleaning until all acceptance criteria are met. These deviations are studied to assess possible causes and corrective actions to bring the cleaning process back to normal control. Preventive maintenance and calibration procedures ensure that equipment and instruments are functioning correctly and in a calibrated state.
Cleaning Validation During biopharmaceutical production, equipment-based cleaning activities play an important role in reducing product contamination. Cleaning validation proves that the cleaning process is adequate and consistent from the cleaned equipment/The system removes product residues, process residues and environmental pollution to ensure product safety. The development of the cleaning process should be in line with the product’s own characteristics, combined with the production process, select equipment and raw materials that match the process route, and well connect the research and development process with the production process, which is the commercial production of the product and subsequent verification and maintenance. The basics.










