Pharmaceutical products are highly regulated commodities, and at all levels of sale/use packaging, identification and coding play a vital role in ensuring consumer safety and brand protection. If there is no clear and easy-to-read information and data, it is impossible to ensure compliance with laws and regulations, the safety of users, and supply chain backtracking costs that can cause losses cannot be avoided.
In the past 2021, a number of well-known pharmaceutical giants in North America alone (data from www.fda.gov) recalled their products sold in batches, including missing product information, wrong specification labeling, wrong dosage labeling, unreadable information, untraceable data and a series of problems.
But how can we ensure the correctness of product coding and reduce the cost of accidental losses without affecting the efficiency of the production line? There is a principle we can refer to: the earlier a problem is discovered, the less impact it will have. At the same time, there are several aspects that should be taken into account at least:
1. The Standard Specification Of The Product Packaging Itself.
Production of packaged products in only one and multiple sizes may face different technical choices. Sometimes, the difference between them will be very large. From the point of view of coding technology, if the ink coding adopts high resolution, the printing distance requirement will be very close. If laser technology is used, whether the zoom function is still required due to the change of the printing surface, or the transmission system can be compatible with the adjustment of various specifications.
2. Information Content To Be Marked On Product Packaging.
This is closely related to the design of drug packaging, whether to print only the three-phase or drug traceability code on the packaging, a one-dimensional barcode or a GS1 GTIN code that needs to include a two-dimensional code, etc. What is the typesetting design of these information, the size arrangement of characters, the use of encoding rules for QR codes, and how the matrix size is considered (although the information is the same but using different encoding rules will affect the size of the QR code). What are the compliance requirements for coded information? Do you export abroad and consider the different rules of each country to require FDA, FMD, KNIH, SDC, DGFT, ANVISA, ITS?
3. The Material Used For Product Packaging.
Even if it is a paper outer box, the coating and non-coating will directly affect the effect of the coding technology. Uncoated cartons have good permeability, so alcohol or water-based inks can be considered for printing, while coated cartons need to be operated with fast-drying solvent-based inks. Or it is applied by laser burning technology, but it may have a great influence on the contrast effect of different materials after burning. This will increase the difficulty of identification for subsequent check segments. And different coding technologies are accompanied by different printing speeds, and whether different coding qualities can meet the needs of customers should be considered clearly.
4. Requirements For Visual Verification/Inspection.
Potential faults and problems always exist, and it is a key node for the coding inspection of pharmaceutical packaging that can be found immediately after a problem occurs. The sooner a problem is found, the more complexity and even the loss of processing will be reduced. Then, after the packaging and coding process of pharmaceutical products, the importance of following visual inspection is self-evident. But the question is, for visual inspection, what are we testing for? Is there a code? Missing part of the code? Can the barcode/QR code be read? These are just the basics. Next, we consider that the QR code can be read, but what is its level? If it is incorporated into the subsequent work section or may be worn/attenuated during transportation (the speed of ink light fading), light reading may not be enough. Is there also a requirement for code level detection? Not finished yet, do you consider whether the content verification of all characters except barcode/QR code can be read? Is the content that should be correctly coded after reading consistent with the plan? This is the result we want to achieve, but the technical implementation also needs to consider the characteristics of different coding equipment, such as scribing laser, high-resolution thermal foaming, dot matrix continuous inkjet, and printing-like thermal transfer, etc. They produce different image characteristics and character edge types, and even show different “failures” when there are coding failures. For the visual verification process section, it requires a certain amount of technical experience and time to improve the recognition image learning process in different situations.
5. Data Association Considerations.
In simple terms, from coding to visual inspection, the input and output of data are related to the consideration of the entire system. If it is a requirement of one item, one code, whether the data of the current packaging level still needs to be correlated, from the single product to the middle package to the outer box stacking pallet, this series of data correlation needs to be considered, and from the very beginning of the samll packaging code inspection, it is necessary to ensure a very high degree of correctness.
6. The Operation Process Of Defective Products.
Without 100% OEE (Overall Comprehensive Production Efficiency), there will always be various problems leading to wastage and defective products. In the process of packaging and coding, when such a situation occurs, in addition to being able to detect it in time, it is very important to be able to deal with it as soon as possible. If there are more levels of association in the future, once the queue is confused, it will be troublesome. The operators at the scene will be confused, desperately looking for defective products or even scrapping a large section of products. Accurate, fast, and correct corresponding rejections should be taken into consideration, and data feedback for coding defective products, and image storage or uploading for visual inspection should be improved.
7. Compliance Certification.
Different from other products, pharmaceutical manufacturing has extremely strict compliance requirements. From equipment operation to digital signatures, from the composition of coding ink to GMP production, every flaw may affect the overall compliance of pharmaceutical products. . Does the coding detection function used have/meet 21 CFR part11, ePedigree? Do the marking ink products used also comply with GMP production standards? Careful consideration is also required.
Domino’s pharmaceutical packaging coding and testing solutions fully consider the above 7 points, which can help companies ensure the correctness of product coding and greatly reduce production line costs. Domino has more than 40 years of experience in solutions in pharmaceutical product traceability, GMP compliance and combating counterfeit drugs, and has always adhered to the “Do More” concept, users can fully trust the entire coding and identification process it provides. It can be said that they are experts in “mark” and “recognition”, and can provide users with one-stop solutions, including:
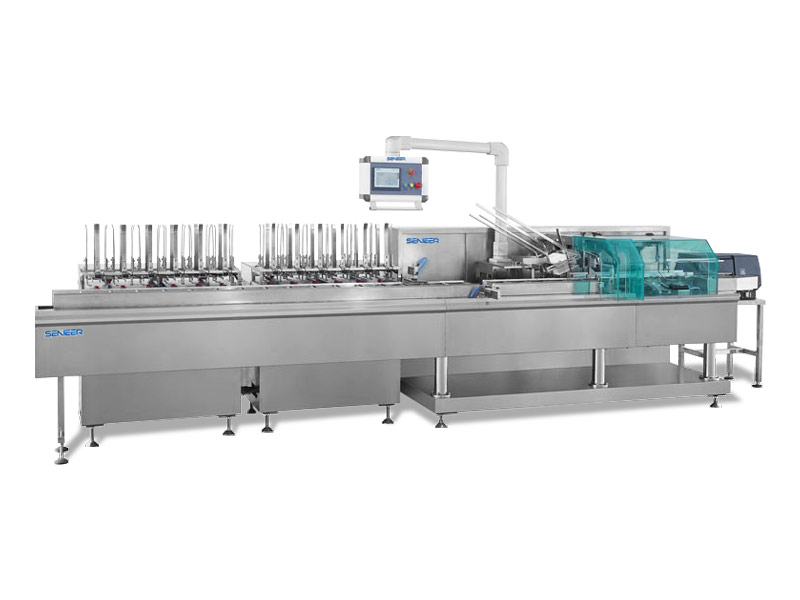

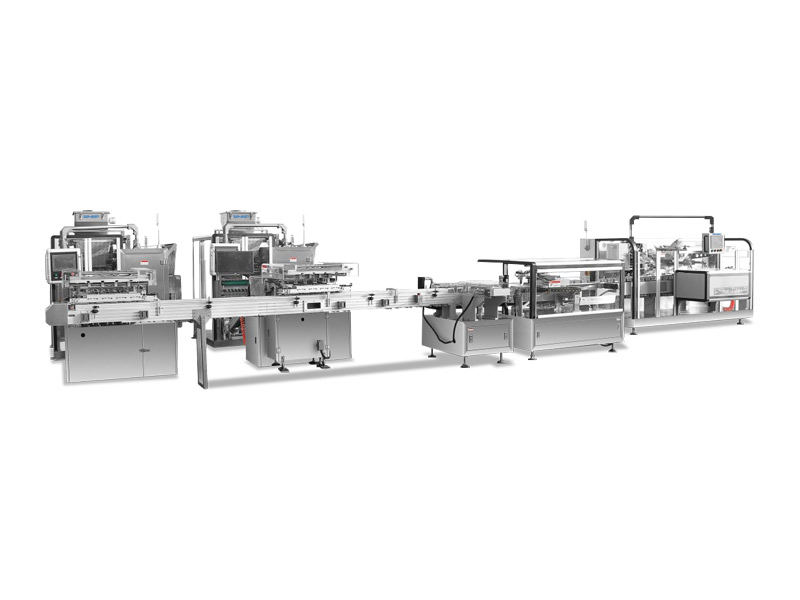
Domino’s One-Stop Solution For Visual Inspection Of Outer Box Coding
Domino’s printing visual workstation (CV Station) is used for serialization information of box packaging, including printing of various barcodes, QR codes, batch numbers, product identification numbers (GS1\GTIN), expiration dates, pattern logos, etc., and at the same time At the same time, it includes a visual inspection system to meet the functions of MRC and ORC and the solution of rejection of defective products.
There is no need to spend extra effort in coordinating the integration of various equipment manufacturers. This is a mature and efficient outer box coding solution. After understanding the reserved stations of the production line, we will customize the printing vision workstation that matches the size of the line body and seamlessly integrate it into you planned line body station.
Serialized Information Printing
- 1D code, 2D code, batch number, expiration date and product identification number (eg: GS1 GTIN)
- Compliant with ISO/IEC 15415 barcode level detection
- Up to 400 boxes per minute production rate
- Automatically save serial number and lot number data
Quick Integration Into Your Production Line
- Develop suitable process parameters according to your production line
- Line speed up to 60 m/min
- Synchronous upper and lower clamping conveyor belt design, stable and precise
- Compatible with permeable or non-permeable packaging materials
- High-speed pneumatic rejection of defective products
Powerful Visual Inspection Capabilities
- Drug code content check
- MRC and ORC identification detection
- Defective product inspection image saving or uploading
- Online Code Level Detection (ABCDF) (optional)
- 21 CFR Part 11 compliance










