Several Suggestions On The Setup And Use of Continuous Monitoring System In Cleanroom
GMP Good Manufacturing Practice for Pharmaceuticals and GAMP Automated Production Quality Management Practice are more and more strict on the standards, technical specifications and regulations implemented in the pharmaceutical production process, and they must be certified by the QM quality management system, and the installation of monitoring system meets the special requirements and regulations for the production of pharmaceutical products is necessary. In this article, we will analyze how cleanroom can work efficiently under GMP standards.
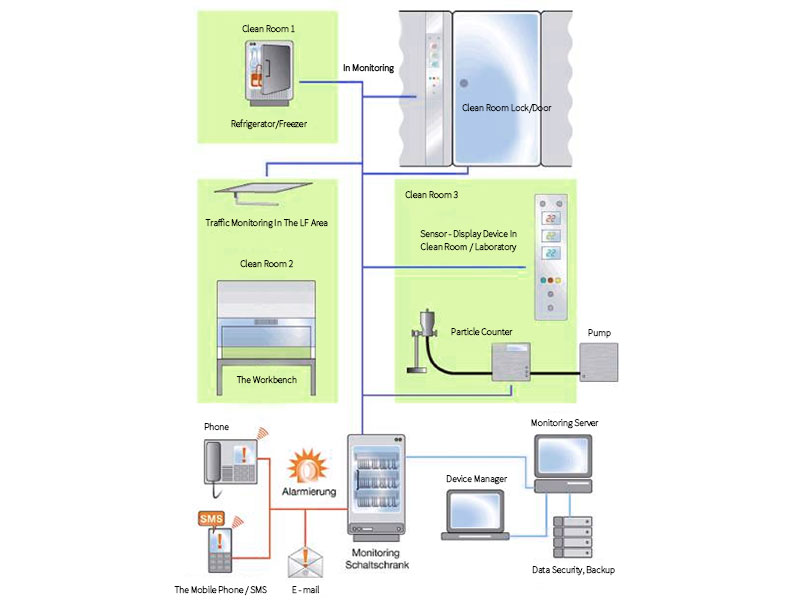
The basic structure of the integrated monitoring system consists of the following main parts and modules:
- Sensors that collect parameters and data.
- Display equipment (display, touch screen, indicator light) for visualization inside the clean room.
- Alarm system (phone, email, SMS).
- Data security and data backup system for long-term preservation of data and file records.
- Simple software system for reaction, analysis and recording.
On the premise of not increasing the workload of production operators, the monitoring system can automatically and strictly record environmental data and production data continuously and without defects. In this way, on the one hand, the user can take corresponding measures according to the change of the parameters, and on the other hand, the historical data of clean room work can be saved for a long time. In order to use the monitoring tools smoothly, it is necessary to take into account the problems that may be encountered during the entire life cycle at the beginning of the clean room design, to ensure that the monitoring system will not accidentally “drop the chain”, to provide favorable support and assistance to users in their daily work, and to reduce the tedious work records workload.
No specific technology is required for such planning and design, as this monitoring system is almost universal. It is important to note that the system should meet the requirements of the production process, the product and the current standards. When designing a monitoring system, you must first answer the following questions:

- Which requirements and regulations of existing standards and technical specifications should be observed? The standards, specifications and requirements here refer to, on the one hand, related to product production and certification inspection, and on the other hand, refer to the requirements that the monitoring system should pay attention to.
- What are the tasks to be completed and the problems encountered in the future? The key words here are: future development possibilities, maintenance conditions, metrological verification performance, certification status.
- In what range is it feasible to use a single parameter, and in which range is integrated monitoring required?
- How can the system be configured to maximize operator assistance?
In order to obtain a production license, the regulations and requirements of GMP, GAMP and FDA must be complied with, from the planning and design of the monitoring system to the production and use operation.
Design Task Book
Cleanroom design begins with a URS design brief. There are three main factors to keep in mind when determining the basic requirements of a cleanroom:
- The production process of the product (clean room class, safety requirements, location).
- product risk (sensitivity to temperature, humidity).
- Requirements for monitoring.

With the increase of personalized needs, other auxiliary requirements put forward by users are also increasing. E.g:
- Materials: Stainless steel testing equipment, a wide range of integrated systems (keyword: hygienic design).
- Sensor quality: What should be the error margin of the sensor? Are there any sensors that require high precision, such as refrigerators or freezers?
- Design: Where should an alarm system for operators in the cleanroom to inform their peers in the production process be installed?
At this point, those who work with the system in the cleanroom must be involved in the design process to address the above issues.
After the requirements for the cleanroom monitoring system have been determined, the system supplier must be given a list of requirements that clearly defines the responsibilities of the system supplier. This list is subject to review by the contract principals and, if necessary, revisions by them. Then, the system supplier implements these requirements after completing the production and manufacture of the product, and conducts the FAT factory acceptance test, and the user understands the quality of the entire monitoring system product before the monitoring system is installed.
Technical Training
After completion of the FAT Factory Acceptance Test, the supplier is ready to install in the user’s clean room for IQ installation quality certification, OQ functional certification, and GMP compliant on-site inspection. An important issue to note here is the technical training of cleanroom operators, allowing operators to learn how to use and operate the system directly in the installed monitoring system.
After completing the installation, commissioning and certification inspection, the monitoring system can be officially put into production. According to the requirements and regulations of GMP, the service life of the monitoring system is longer. The monitoring system shall be maintained within the specified maintenance cycle (usually once every 12 months), and the sensor shall be measured and verified. It is worth noting that the monitoring system should be able to be maintained in the installed state, which is also a problem that must be considered in the design. All sensor components, including the entire detection chain, are subject to metrological verification and calibration if necessary. The maintenance must be carried out in accordance with the maintenance plan, and maintenance records must be kept.
If changes or expansions are to be made to the cleanroom monitoring system during its use and operation, it must be done in accordance with the prescribed (change control) standards and documented. Such changes can be functional control due to the connection of incubators and coolers, or changes in limit values due to the production of other products, etc. In this case, the design and construction should be carried out in accordance with the regulations and requirements of GMP, and corresponding records should be made to ensure that the monitoring system can pass the certification inspection.











