This paper introduces several sterilization methods of sterile drugs : humid heat sterilization, dry heat sterilization, radiation sterilization, ethylene oxide sterilization and sterilization filtration, studies the sterilization principle, influencing factors, advantages and disadvantages of various sterilization methods, and products suitable for sterilization, etc., and selects the decision tree as the sterilization decision-making method of sterile drugs through solution-form products and dry powder products or semi-solid, non-solution dosage form sterilization methods.
1 Overview Of Sterilization Of Sterile Drugs
Sterilization method refers to the use of physical and chemical methods to kill or remove all surviving microbial propagules or spores, so that the sterilized items to achieve sterility. In the production of sterile drugs, the prevention of endotoxin pollution and microbial pollution has always been the focus of regulatory agencies and production enterprises. The sterilization of sterile drugs should be to remove or kill the spores and microbial propagules in the drug, so as to ensure the safety of the drug itself, and must also ensure the stability of the drug and its clinical treatment effect, so the production enterprises of these sterile drugs use appropriate sterilization methods, which is of great significance to the guarantee of drug quality.
2 Introduction To Sterilization Methods For Sterile Drugs
2.1 Humid Heat Sterilization
Humid heat sterilization refers to the use of high-pressure steam or other thermodynamic sterilization methods in the sterilizer to kill microorganisms in the article. Humid heat sterilization is one of the most widely used and effective methods in thermodynamic sterilization, with the characteristics of fast conduction, strong penetration and stronger sterilization ability. At present, the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the United States Pharmacopoeia, the European Pharmacopoeia, and the GMP specifications of various countries all include this method. Principle: Humid heat sterilization is to denature the nucleic acid and egg white matter of microorganisms by means of damp heat, resulting in their death. This denaturation is that the hydrogen bond in the molecule first splits, and then the internal structure of the nucleic acid and the protein is destroyed, so that its original function is lost and the purpose of sterilization is achieved.
Factors affecting the damp heat sterilization effect include :
(1) The length of time required for sterilization is related to the number of microorganisms in the initial sterilization, so according to the first-order dynamic equation, the number and type of microorganisms in the sterilization directly affect the sterilization effect.
(2) In general, the heat resistance of microorganisms in neutral solutions is the best, poor in alkaline solutions, and the worst in acidic solutions, so the pH of the sterilization solution is also a factor affecting the sterilization effect.
(3) The nature of the sterilized substance, if the solution contains amino acids and sugars and other nutrients, microorganisms will be protected by these nutrients, thereby enhancing their heat resistance.
(4) The penetration of dry hot air and superheated steam is much worse than the penetration of saturated steam, so the saturation of steam is another influencing factor of the sterilization effect, and saturated steam should be used as much as possible for sterilization.
2.2 Dry Heat Sterilization
Dry heat sterilization is a method of killing microorganisms by making deoxyribonucleases, microorganisms and other biological polymers produce non-specific oxidation at high temperatures. According to the different ways of use, dry heat sterilization equipment can be divided into continuous and intermittent, such as tunnel sterilization oven is continuous, for the sterilization of vials or ampoules; The dry heat sterilization cabinet is intermittent and can be used for sterilization and heat removal sources of equipment parts and metal appliances. The thermodynamic principle of dry heat sterilization is similar to that of damp heat sterilization, and the killing of microorganisms also meets the logarithmic principle under certain sterilization conditions. High-temperature powder chemicals and some metal equipment, greases and utensils that do not require moisture penetration, as well as high-temperature-resistant items such as glass can be considered dry heat sterilization, but not suitable for most drugs, plastics and rubber sterilization, dry heat sterilization can also remove heat sources. For example, in the production workshop of sterile drug water needles, some appliances in the B and C class clean areas can be sterilized by dry heat using electric heating through double-sided dry heat sterilization cabinets.
2.3 Radiation Sterilization
Radiation sterilization is the use of ionizing radiation to kill microorganisms sterilization method, for sterilization of electromagnetic waves such as microwaves, ultraviolet rays, γ rays, X-rays and the like. At present, radiation sterilization mostly uses γ rays emitted from 60Co sources. Principle of the radiation sterilization process: In a specially designed device, the product is exposed to γ rays produced by cobalt 60 (60Co) radionuclides, cesium 137 (137Cs) radionuclides, or electron or X-ray beams generated by electron generators, thus achieving a method of killing microorganisms.
Radiation sterilization has the following advantages:
(1) Normal temperature sterilization, the temperature rise during product sterilization is small, suitable for the sterilization of heat-sensitive biological products and drugs.
(2) The process is simple, once the sterilization parameters are determined, time is the only adjustable factor, suitable for industrial large-scale production, saving energy, and not polluting the environment.
(3) After packaging and then sterilization, under sealed packaging conditions, the product can remain sterile for a long time.

(4) The penetration of radiation is very strong, its sterilization is also thorough, and it is not limited by the packaging and form of the article.
(5) There are no radioactive residues, no chemical toxicity and other side effects in the irradiated products.
2.4 Ethylene Oxide Sterilization
Ethylene oxide sterilization, it is a relatively reliable low temperature sterilization method. Ethylene oxide has an unstable ternary ring structure and its small molecular properties, making it highly penetrating and chemically active. Common ethylene oxide sterilization processes use vacuum processes, which can generally use 100% pure ethylene oxide or gas mixtures containing 40% to 90% ethylene oxide (e.g., mixed with carbon dioxide or nitrogen). When using a positive pressure process, 8% to 20% ethylene oxide is mixed with carbon dioxide gas. The product is sterilized in a pressurized chamber filled with sterilizing gas. The sterilization process of standard ethylene oxide consists of 3 different stages: pretreatment, sterilization and resolution. Principle of ethylene oxide sterilization: Ethylene oxide is a broad-spectrum sterilizer that can kill fungi, spores, viruses, bacteria and other microorganisms at room temperature; It can alkylated with amino, hydrogen thiide, carboxyl, etc. on proteins, resulting in microbial death; It can also inhibit the biological enzyme activity of cholinesterase, cholinase, peptidase, phosphoparasidase and the like; Ethylene oxide can also react alkylated with RNA and DNA to lead to microbial inactivation.
2.5 Filter Sterilization
Sterilization filtration refers to the process of removing microorganisms from a fluid through a filter that should not adversely affect product quality. Includes liquid and gas sterilization filtration. The sterilization filtration of liquids in the production of sterile drugs generally adopts the pore size of the sterilization filter membrane not exceeding 0.22 μm, which can achieve an effective filtration area per square centimeter and intercept 107CFU defective Pseudomonas under process conditions, which is the general requirement of liquid sterilization filters. Many sterile products that are finally sterilized use filters to filter the products before filling before final sterilization, controlling the level of microbial contamination; For sterile products that cannot be finally sterilized, such as some sterile water needles, lyophilized powder needles, etc. filter the products by sterile filtration before filling to achieve a sterile level. Considering reducing the risk of sterilization filtration, when 1 sterilization filter can achieve the sterilization filtration effect, add the second (or use multiple) sterilization-level filters to ensure the effect of sterilization filtration, such a setting is often referred to as “double” or “redundant” setting.
3 Sterile Drug Sterilization Decisions
Sterile drug sterilization needs to choose different methods according to the situation, generally considering the purpose of use, the stability of the sterilization object and the specific conditions in production. For example, glass containers generally use dry heat sterilization treatment, environmental facilities should be treated by chemical sterilization, and rubber products and clothing are generally used in humid heat sterilization, and lactose, Chinese medicine powder and other powders can be selected for radiation sterilization treatment. Formulation products usually need to choose a suitable sterilization method according to the characteristics of the product.
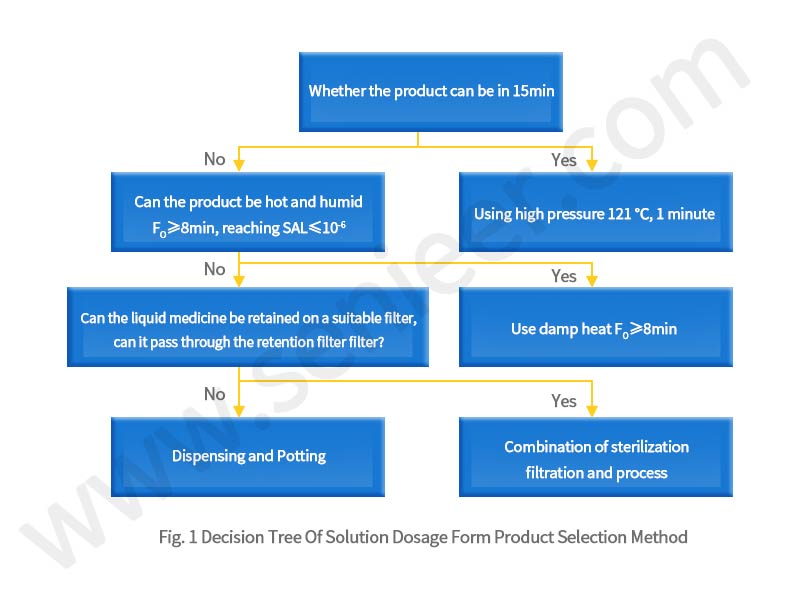
The following takes the decision tree for the selection of sterilization process of solution dosage form products, dry powder products, semi-solid or non-solution dosage forms as an example (Figure 1), as a choice tree for sterile drug sterilization method selection, sterile drug manufacturers can be used as a reference when choosing a sterilization method.
4 Conclusion
Preventing endotoxin contamination and microbial contamination has always been the focus of attention of regulators and production enterprises on the production of sterile drugs. The choice of sterilization method is of great significance for the safety, stability and clinical efficacy of drug preparations, so production enterprises should choose their own sterilization methods from the characteristics of their production products and various restrictions, with reference to the sterilization method selection decision tree.










