Biological products are preparations for the prevention, treatment and diagnosis of human diseases, such as vaccines, blood products, biotechnology drugs, probiotics, immunomodulators, diagnostic products, etc. [1]. Among them, therapeutic biological products have gradually become the development focus of the global pharmaceutical industry in the past decade. Eight of the top 10 blockbuster products in global annual sales are therapeutic biological drugs [2-3]. As the production site of biological products, the design of the clean workshop for biological products should not only meet the special process requirements of biological products, but also consider the requirements of fire regulations, energy saving, personnel and environmental protection. Therefore, the preliminary design of the biological product clean workshop needs to comprehensively consider many factors. With the implementation of GMP and the development of the pharmaceutical industry, many problems have been exposed in the practical application of biological product clean workshops. Part of the problem is due to the lack of comprehensive consideration in the design process of the biological clean room. Starting from the guarantee of the quality of medicines, this paper makes statistics and analysis of the problems existing in the preliminary design of 12 biological product clean workshops from the perspective of the 2010 version of GMP, and then puts forward suggestions, which hope to provide reference for the preliminary design of biological products clean workshop.
1 Overview Of Frequently Asked Questions
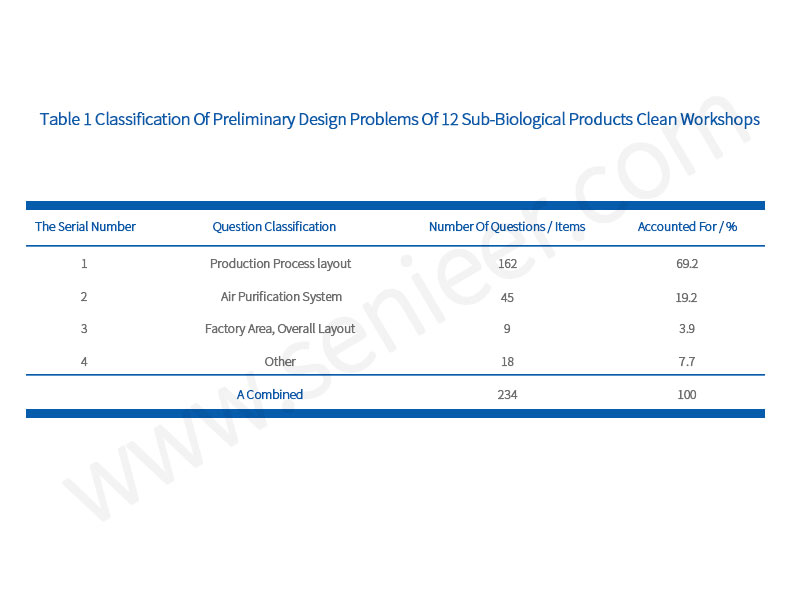
A total of 234 problems were found in the preliminary design of the 12 biological product clean plant systems, and they were classified according to the frequency of the problems: (1) The layout of the production process, such as the flow of people and the poor design of the logistics; (2) In the air purification system, the pressure difference setting and the exhaust air setting is unreasonable, etc.; (3) The overall layout of the plant is unreasonable, mainly in the site selection and layout of the plant; (4) Other problems, such as improper water system and electrical system settings, etc. See Table 1 for details.
2 Problem Analysis
2.1 Production Process Layout
It can be seen from Table 1 that the production process layout problems occurred most frequently, with a total of 162 items, accounting for 69.2% of the total. These problems are likely to directly affect the quality of medicines. If the flow of people and logistics is unreasonable, it is easy to cause product contamination, cross-contamination and personnel cross-posting. Unreasonable regional planning may interfere with normal production, and at the same time, it is inconvenient for daily monitoring and observation.
2.1.1 Poor Flow Of People And Logistics
Article 40 of the GMP standard requires that the people and logistics in the factory area and the factory building should be reasonable [4]. Part of the design flow of people and logistics design is not smooth, which is easy to cause confusion, errors and pollution. If the waste from the filling area needs to pass through multiple operation rooms, and finally pass out of the clean area through the material introduction channel, the operation is inconvenient and it is easy to cause pollution and cross-contamination. The waste exit route should be redesigned. Some designs have the phenomenon that operators pass through other operating areas. For example, personnel in the fermentation centrifuge room need to pass through the fermentation room and the bacterial collection room, and personnel in the freeze-thaw position need to pass through the purification and centrifuge room. Such an arrangement will not only lead to inconvenience in operation, but also easily lead to personnel cross-posting and cross-contamination. The operator should set the post according to the actual production, so that the personnel do not cross the post and avoid detours. The process layout of the biological product clean workshop should be arranged according to the production process and operating procedures, so that the flow of goods and people are smooth, and the flow of people and logistics is reasonably separated [5].
2.1.2 Unreasonable Regional Planning
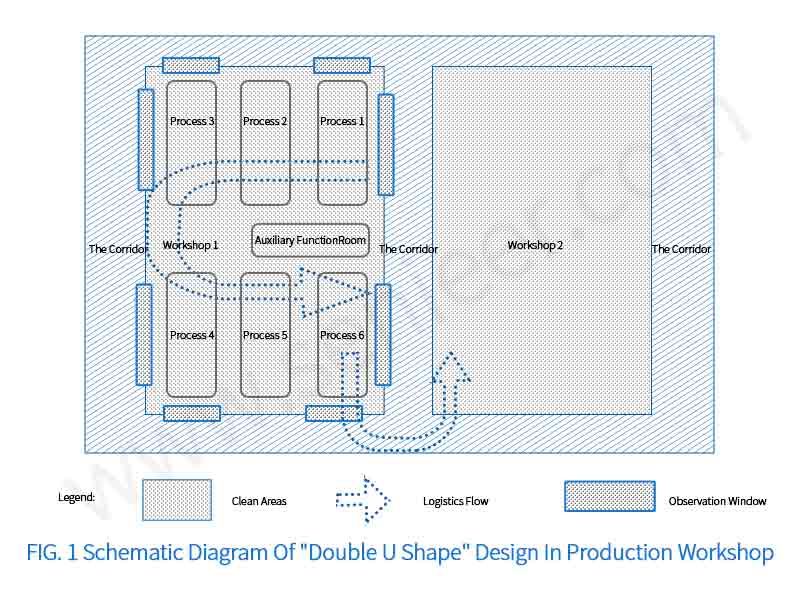
Some designs arrange key processes in the inner center of the workshop layout, such as virus inactivation, filling and other processes. Non-production personnel (such as quality assurance personnel) need to enter the core area for daily monitoring and observation, which may cause interference to production. At the same time, it is not conducive to the development of medium simulation filling and deviation investigation. The ideal design of the production workshop is the design of long-strip assembly line operation, but the production enterprises generally do not have enough space to build such a workshop. Part of the design achieves the above effect through the “U-shaped” arrangement: the key processes are set on the periphery of the workshop layout (as shown in Figure 1), and the auxiliary workshop is designed in the middle. Through this design, non-production staff can view key processes through the observation window. Observations are made without disturbing normal production. At the same time, the workshops of the front and rear processes can also be connected through the “U-shaped” design, such as the stock solution workshop and the preparation workshop of vaccine products. Through this design, the flow of people and logistics routes can be optimized, and the transportation distance of materials can be minimized.
2.1.3 The Selection Of Production Equipment Is Not Suitable For Production Needs
Article 49 of biological products in the appendix of GMP specification requires: When using pathogens of class II or above for production, the generated dirt and suspected contaminated items should be disinfected in situ, and can be removed from the work area after complete inactivation [6]. Part of the design does not consider the transmission method of items in the operation area with bacteria (toxic), and lacks corresponding supporting equipment. If there is solid waste and waste liquid produced in the production process of bacterial (toxic) operation area, there may be inactivated bacteria. Therefore, all the items involved in this operation area, such as work clothes, utensils, discarded harvest liquid, waste water from CIP stations, etc., need to be inactivated by proven methods, and the production germs can be killed before leaving this area. Solid waste such as stainless steel utensils, work clothes, etc. can be sterilized by steam autoclave and then passed out [7]. Appliances that cannot withstand high temperature and high pressure, such as thermometers, pressure gauges and other precision instruments, can be sterilized by a vaporized hydrogen peroxide sterilizer (Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide/VHP), and some designs are sterilized by ozone fumigation. It should be evaluated whether it can achieve the expected sterilization effect.
2.2 Air Purification System
The main purpose of an air purification system is to ensure the ambient air quality of biological products and to prevent cross-contamination. If the pharmaceutical production environment is properly designed, constructed, commissioned, operated and maintained, it will help to ensure product quality and improve product reliability [8]. It can be seen from Table 1 that there are 45 problems in the air purification system, accounting for 19.2%, such as unreasonable pressure difference setting and unreasonable exhaust setting.
2.2.1 Improper Differential Pressure Setting
Article 48 of the GMP specification requires that the pressure difference between the clean area and the non-clean area and between the clean areas of different cleanliness levels should not be less than 10 Pascals. When necessary, an appropriate differential pressure gradient should also be maintained between different functional areas (operating rooms) of the same cleanliness level [4]. Some designs do not consider the requirements of special varieties for negative pressure gradient, and there is the problem of pressure gradient fluctuation caused by the system variable air volume process (such as biological safety cabinet start and stop, standby supply/exhaust fan unit switching, etc.). The difference air volume control method is used to adjust the difference between the supply air volume and the exhaust air volume of each room to ensure the pressure gradient of each room, which can better solve the above problems [9]. At the same time, the design should consider the size of negative pressure gradient and energy saving. When there is a large negative pressure, it can effectively prevent the leakage of pathogenic biological factor aerosols, but the construction cost and operation cost are high; on the contrary, when the negative pressure is small, it is easy to produce aerosol leakage of pathogenic biological factors, which will cause safety problems to the production area and the outside [10].
2.2.2 Unreasonable Ventilation Setting
GMP standard appendix biological products Article 22 requires: There should be an independent air purification system in the bacteria (toxic) operation area. The air from the pathogen operation area shall not be recycled; the air from the pathogen operation area with a hazard level of two or more should be discharged through a sterilizing filter, and the performance of the filter should be checked regularly [6]. The air in some of the designed pathogen operation areas is not discharged after treatment. The air in this area is generally treated in a straight-line manner, and no return air is used, and the toxic area can be set as close to the power area as possible to achieve the purpose of energy saving.
2.3 The Overall Layout Of The Factory Area Is Unreasonable
It can be seen from Table 1 that the preliminary design of some biological product clean workshops still has the problem of unreasonable overall layout of the plant area. Although it only accounts for 3.9%, such problems are not easy to adjust and rectify after the project is implemented. If the site is improperly selected, the harmful gases emitted around the factory area are likely to cause pollution to drug production. The layout of the factory area is improper, and the living and auxiliary areas hinder the production area. It shows that there are still large loopholes or defects in the overall planning.

2.3.1 Improper Site Selection Of The Factory
Article 38 of “Good Manufacturing Practice for Drugs” (revised in 2010, referred to as GMP) requires that the site selection, design, layout, construction, renovation and maintenance of the workshop must meet the requirements of drug production, and should be able to avoid pollution, Cross-contamination, mix-ups and errors, ease of cleaning, operation and maintenance [4]. The site selection of some preliminary designs is unreasonable. For example, the site selection of an enterprise is located near the petrochemical industrial zone, and the harmful gases emitted by the petrochemical industry are likely to cause pollution to the production of medicines. When selecting a site for a biological product manufacturer, it should stay away from places that emit a lot of dust and harmful gases, so as to avoid the harmful gases that are easily cause pollution to drug production. The site selection of a pharmaceutical production enterprise is the first step in pharmaceutical production planning. Enterprises should comprehensively consider factors such as their own development and the direction of regional planning to avoid congenital deficiencies in the preparation of the factory.
2.3.2 Improper Layout In The Factory
Article 40 of the GMP standard requires that the overall layout of production, administration, living and auxiliary areas should be reasonable and not interfere with each other [4]. Part of the preliminary design has comprehensive activity buildings, canteens and other supporting facilities in the production area, and appropriate spacing measures should be added to separate the production area and the living area in the factory area without affecting each other. In addition, some designs have only one primary cell bank and do not consider alternate primary cell banks. “Procedures for Preparation and Verification of Animal Cell Matrix for Production Verification of Biological Products” requires that the main cell bank and the working cell bank should be stored separately. Each library should be housed in at least 2 different locations or areas within the production facility [1]. As the starting material of biological products, the master cell bank is the material basis for pre-market clinical evaluation and post-market research of biological products. The research process is long and complicated. Therefore, the master cell bank is the basis for the survival and development of biological product manufacturers. Enterprises should strengthen the protection of the main cell bank to ensure that the main cell bank can take effective measures in the event of a power outage, fire and other emergencies.
2.4 Others
There are 18 other problems, accounting for 7.7%, mainly involving drainage system problems and electrical system problems.
2.4.1 Water System Aspects
Water is the carrier of many biological products. Once it is polluted, the consequences will be disastrous [11]. Some designs do not consider the requirement that the preparation and storage of water for injection must prevent the growth and contamination of microorganisms. For example, the water for injection can be used in a heat preservation cycle above 70 °C [4] and used within a specified time after preparation. At the same time, in order to ensure biological safety, the waste liquid in the toxic area must be sterilized before treatment. For example, a waste liquid inactivation room is set up in the basement, and the drainage pipes are respectively connected to the inactivation tank of the waste liquid inactivation room. After live treatment, it is discharged to the sewage treatment station in the plant area, and then discharged after treatment.
For the public systems of biological products manufacturing enterprises, such as water systems and air supply systems, after the system is emptied, air passages will be formed in the pipelines. Viruses and pathogenic bacteria can pollute other systems and the environment through the pipelines. Viruses and pathogens should be prevented. Bacteria contaminate other systems and environmental measures in this way. In addition, the pipelines should be separated as much as possible during the supply of the public works system in the toxic area and the non-toxic area to prevent cross-contamination [12].
2.4.2 Electrical System Aspects
Article 79 of the GMP specification requires that the maintenance and repair of equipment shall not affect product quality. Routine maintenance and repair of production equipment in the workshop is an indispensable part of ensuring the quality of medicines, but routine maintenance and repair may adversely affect the environment in the workshop and even affect the quality of products. In some designs, power distribution cabinets, fire hydrants, etc. are set in the clean area, which is inconvenient for daily maintenance and repair. Under the premise of meeting fire protection and industry regulations, power distribution cabinets and fire hydrants should be installed in non-clean areas and non-toxic areas as much as possible [13].
In addition, there is a problem of exposed pipeline tissue in some designs, which is inconvenient for cleaning and maintenance in the clean area. The pipeline organization in the clean workshop should be planned together with the layout of various computer rooms, and different concealment measures should be taken. If the pipeline shaft is used as the vertical concentration space of various pipelines, it should be arranged adjacent to the machine room as much as possible. The technical interlayer is used as the horizontal dispersion space of the pipeline, which should provide enough space for the passage and maintenance of the pipeline [13].

3 Summary
Due to the particularity of its production varieties, the biological product clean workshop determines the complexity of the process flow design and the special requirements of the public system. These characteristics put forward higher requirements for the preliminary design of the biological product clean workshop. In addition to meeting the basis of the production process requirements, factors such as biosafety, fire protection, and environmental protection regulations should also be considered. The biological product manufacturer should fully communicate with the designer so that the designer can fully understand the production process, the positioning of the project and the special requirements of the manufacturer. We should, according to the production process and operating procedures, scientifically and reasonably carry out the plane layout and equipment layout, minimize errors and cross-contamination, continuously explore, analyze and summarize in the design process, and design a more optimized solution.










